Vegeta压测工具学习与使用
Vegeta压测工具学习与使用
目标:
- 能够在命令行下使用Vegeta对指定API进行测试
- 了解如何导出结果,以及能获得什么样的结果(P99,P99.9,QPS)
- 探索能否导出其他结果,是否能够执行复杂命令或简易脚本等
时间比较紧迫,预计两到三个小时内完成
参考资料:
安装
在确定GOBIN在PATH内时,直接使用go get -u github.com/tsenart/vegeta 即可完成安装。
简易使用
在iris服务器中开启一个简单的router
app.Get("/test/{name}",func(ctx iris.Context){
name := ctx.Params().Get("name")
log.Println(name)
})声明一个简单的txt(必须带上HTTP)
GET http://localhost:8080/test/name1
GET http://localhost:8080/test/name2
GET http://localhost:8080/test/name3执行命令vegeta attack -targets ./test.txt -duration=30s -rate=10000 > result.bin,即可开启服务,进行测试。(PS:不知道为什么-rate=0不支持,会报错误要求一个大于0的数)
执行vegeta report result.bin即可拿到执行报告
Requests [total, rate] 300000, 9985.22
Duration [total, attack, wait] 31.3856523s, 30.044419s, 1.3412333s
Latencies [mean, 50, 95, 99, max] 1.367112453s, 4.50456ms, 4.511788108s, 6.305999861s, 7.6157462s
Bytes In [total, mean] 0, 0.00
Bytes Out [total, mean] 0, 0.00
Success [ratio] 48.38%
Status Codes [code:count] 200:145132 0:154868
Error Set:
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name3: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: bind: An operation on a socket could not be performed because the system lacked su
fficient buffer space or because a queue was full.
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name1: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: bind: An operation on a socket could not be performed because the system lacked su
fficient buffer space or because a queue was full.
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name2: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: bind: An operation on a socket could not be performed because the system lacked su
fficient buffer space or because a queue was full.
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name1: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: connectex: Only one usage of each socket address (protocol/network address/port) i
s normally permitted.
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name2: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: connectex: Only one usage of each socket address (protocol/network address/port) i
s normally permitted.
Get http://localhost:8080/test/name3: dial tcp 0.0.0.0:0->[::1]:8080: connectex: Only one usage of each socket address (protocol/network address/port) i
s normally permitted.此外还支持golang的库内部链接,例如:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
vegeta "github.com/tsenart/vegeta/v12/lib"
)
func main() {
rate := vegeta.Rate{Freq: 100, Per: time.Second}
duration := 4 * time.Second
targeter := vegeta.NewStaticTargeter(vegeta.Target{
Method: "GET",
URL: "http://localhost:8080/test",
})
//测试的实现需要基于Attacker
attacker := vegeta.NewAttacker()
var metrics vegeta.Metrics
for res := range attacker.Attack(targeter, rate, duration, "Big Bang!") {
//res是Result向量,执行结果。拿到的时候代表一次执行已经结束
metrics.Add(res)
}
metrics.Close()
fmt.Printf("99th percentile: %s\n", metrics.Latencies.P99)
}从golang程序中启动Vegeta
由于需要输入不同的元素或者控制元素的数量,一个想法是直接生成一个百万行的文件并插入,另外一个想法是直接在程序内启动。出于对更灵活的性能的追求,我还是想尝试一下后者。
使用DEBUG单步调试,发现attack.Attack
根据issue中的回复可以看到,只要返回一个能够产生Targeter的函数即可。其中Targeter也是一个函数(类型为type Targeter func(*Target) error,而Target在我的理解中是即将发送的请求,原文为HTTP request blueprint)
而例子中的atacker.Attack的返回值是一个channel,相当于是vegeta attack命令。其中attacker对象由NewAttacker创建,可以指定一些参数(比如最大并行数量等)
Attack分析
// Attack reads its Targets from the passed Targeter and attacks them at
// the rate specified by the Pacer. When the duration is zero the attack
// runs until Stop is called. Results are sent to the returned channel as soon
// as they arrive and will have their Attack field set to the given name.
func (a *Attacker) Attack(tr Targeter, p Pacer, du time.Duration, name string) <-chan *Result {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
//最大并发数的限制由Attacker提供
workers := a.workers
if workers > a.maxWorkers {
workers = a.maxWorkers
}
//返回的结果队列
results := make(chan *Result)
ticks := make(chan struct{}) //ticks是控制速度用的,attack需要消费ticks中的数据才能继续执行
for i := uint64(0); i < workers; i++ {
wg.Add(1)//wait group
go a.attack(tr, name, &wg, ticks, results)//使用go协程来控制。其中results被放入,在其中产生
}
go func() {
//defer的实现上类似于栈,因此是先关闭ticks队列,再等待所有的a.attack函数执行完毕,最后关闭results队列
defer close(results)
defer wg.Wait()
defer close(ticks)
began, count := time.Now(), uint64(0)
for {
elapsed := time.Since(began)//拿到过去的时间
if du > 0 && elapsed > du {//du即为duration,如果持续时间超过则直接结束
return
}
wait, stop := p.Pace(elapsed, count)//Pacer,负责控制速度
if stop {
return //如果发完了,则返回
}
time.Sleep(wait)//等待剩余时间
if workers < a.maxWorkers {//如果并发没有打满
select {
case ticks <- struct{}{}://向ticks中传入数据。由于ticks没有缓冲,所以如果其数据没有消耗掉则不能放入
count++
continue
case <-a.stopch://接受到停止信号,直接中断
return
default:
// all workers are blocked. start one more and try again
// 动态调整并发
workers++
wg.Add(1)
go a.attack(tr, name, &wg, ticks, results)
}
}
select {
case ticks <- struct{}{}:
count++
case <-a.stopch:
return
}
}
}()
return results
}attcker.attack
func (a *Attacker) attack(tr Targeter, name string, workers *sync.WaitGroup, ticks <-chan struct{}, results chan<- *Result) {
defer workers.Done()//完成后返回,除非ticks被关闭不然也不会执行到这里。
for range ticks {//每次要消费ticks的数据才能继续进行
results <- a.hit(tr, name)//数据写入到results channel之中
}
}
func (a *Attacker) hit(tr Targeter, name string) *Result {
var (
res = Result{Attack: name} //最终返回的结果
tgt Target
err error
)
a.seqmu.Lock()//加锁,保证对临街资源a.seq的访问与写入是正确的
res.Timestamp = a.began.Add(time.Since(a.began))
res.Seq = a.seq
a.seq++
a.seqmu.Unlock()//解锁
defer func() {
res.Latency = time.Since(res.Timestamp)
if err != nil {
res.Error = err.Error()
}
}()
// 此处的tr就是传入的targeter的终点,这也解释了这个函数是干什么的
// 传入的tgt实际上没有任何意义,看做是返回值会更好一些
if err = tr(&tgt); err != nil {
a.Stop()
return &res
}
res.Method = tgt.Method
res.URL = tgt.URL
req, err := tgt.Request()
if err != nil {
return &res
}
if name != "" {
req.Header.Set("X-Vegeta-Attack", name)
}
req.Header.Set("X-Vegeta-Seq", strconv.FormatUint(res.Seq, 10))
if a.chunked {
req.TransferEncoding = append(req.TransferEncoding, "chunked")
}
r, err := a.client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return &res
}
defer r.Body.Close()
body := io.Reader(r.Body)
if a.maxBody >= 0 {
body = io.LimitReader(r.Body, a.maxBody)
}
if res.Body, err = ioutil.ReadAll(body); err != nil {
return &res
} else if _, err = io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, r.Body); err != nil {
return &res
}
res.BytesIn = uint64(len(res.Body))
if req.ContentLength != -1 {
res.BytesOut = uint64(req.ContentLength)
}
if res.Code = uint16(r.StatusCode); res.Code < 200 || res.Code >= 400 {
res.Error = r.Status
}
res.Headers = r.Header
return &res
}读取文件设计动态访问
因此,动态访问的实现原理就很明确了:
- 实现一个能够返回targeter的函数,并将id作为参数传入其中,如同这个issue所写的那样,或者这个example code
- 如何让其中的内容不同:
- example code使用了随机数。在我的需求中,我可以将所需要的文件读入其中作为数组,然后使用随机数索引访问。
- 直接使用函数内变量,利用闭包的性质。考虑到targeter每次都会被调用(
attack.go的第365行),因此计数器向上移动的时候就可以实现遍历。
下面做了一个小的demo来展示这个思想,服务端会接受一个/test/nameX作为接受变量,发送端会发送随机的/test/XXX过去。
服务端
package main
import (
"github.com/kataras/iris/v12"
prometheusMiddleware "github.com/iris-contrib/middleware/prometheus"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promhttp"
"math/rand"
"strconv"
"time"
"log"
)
func main() {
app := iris.Default()
registerCuckooFilter(app)
registerPrometheus(app)
app.Listen(":8080")
}
func registerCuckooFilter(app *iris.Application){
filter := cuckooFilter.CuckooFilter{}
test := make(map[string]int,0)
app.Get("/test/{name}",func(ctx iris.Context){
name := ctx.Params().Get("name")
if _,ok := test[name];ok{
test[name] ++
}else{
test[name] = 1
}
ctx.StatusCode(iris.StatusOK)
})
app.Get("/get/{name}",func(ctx iris.Context){
name := ctx.Params().Get("name")
if val,ok := test[name];ok{
log.Printf("key number is %v",val)
}else{
log.Println("key doestn't exist")
}
ctx.StatusCode(iris.StatusOK)
})
//查询
//batch操作
//批量插入
//批量查询
//批量删除
}
func registerPrometheus(app *iris.Application){
m := prometheusMiddleware.New("serviceName", 0.3, 1.2, 5.0)
app.Use(m.ServeHTTP)
app.OnErrorCode(iris.StatusNotFound, func(ctx iris.Context) {
// error code handlers are not sharing the same middleware as other routes, so we have
// to call them inside their body.
m.ServeHTTP(ctx)
ctx.Writef("Not Found")
})
app.Get("/", func(ctx iris.Context) {
sleep := rand.Intn(4999) + 1
time.Sleep(time.Duration(sleep) * time.Millisecond)
ctx.Writef("Slept for %d milliseconds", sleep)
})
app.Get("/metrics", iris.FromStd(promhttp.Handler()))
}压测端
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/rand"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
vegeta "github.com/tsenart/vegeta/v12/lib"
)
func main() {
rate := vegeta.Rate{Freq: 100, Per: time.Second}
duration := 4 * time.Second
targeter := NewCustomTargeter(vegeta.Target{
Method: "GET",
URL: "http://localhost:8080/test",
})
//测试的实现需要基于Attacker
attacker := vegeta.NewAttacker()
var metrics vegeta.Metrics
for res := range attacker.Attack(targeter, rate, duration, "random") {
metrics.Add(res)
}
metrics.Close()
fmt.Printf("99th percentile: %s\n", metrics.Latencies.P99)
}
func NewCustomTargeter(target vegeta.Target) vegeta.Targeter{
//读取id文件
//idData,err := readRealData()
//if err != nil{
// panic(err)
//}
//cachedArray := make([]bool,len(idData))
return func(tgt *vegeta.Target) error {
//其中,tgt是作为指针传入的,是需要被修改的。后续HTTP请求的赋值都是来自tgt,所以看做是另外一个返回值会更好一些
*tgt = target
tgt.URL += "/custom"+strconv.Itoa(rand.Intn(100))
//tgt.Header = http.Header{}
return nil
}
}
func readRealData() ([]string, error) {
//读取id.txt文件
filePath := "../../resources/id.txt"
file, err := os.OpenFile(filePath, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer file.Close()
//数据格式为音频id,字符串`TRA_{albumid}_index`,albumid为6-10位数字,index为5位数字以内
//将其作为字符串读取并写入到slices中
idData := make([]string, 0, 1400000)
buf := bufio.NewReader(file)
for {
line, err := buf.ReadString('\n')
line = strings.TrimSpace(line)
idData = append(idData, line)
if err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
} else {
return nil, err
}
}
}
return idData, nil
}之后,通过发送请求curl http://localhost:8080/get/custom54就可以查看触发的数量。
最终输出结果除了一般的分位点(P99)之外,还有HDR图。
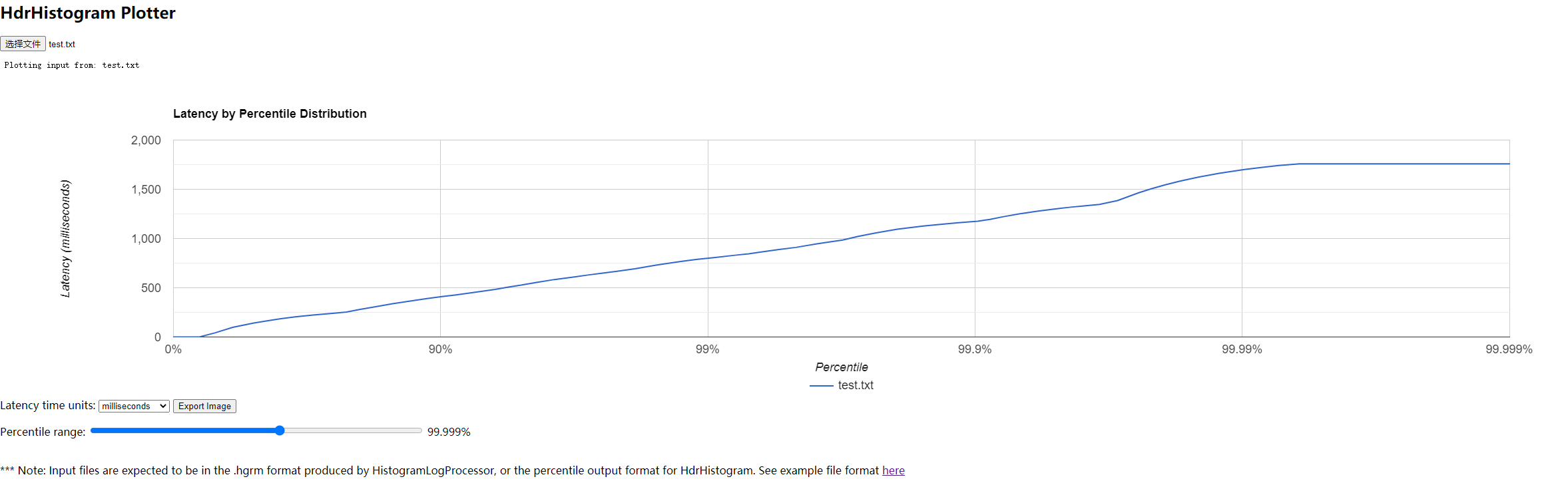
Value(ms) Percentile TotalCount 1/(1-Percentile)
0.000000 0.000000 0 1.000000
0.000000 0.100000 800 1.111111
0.000000 0.200000 1600 1.250000
41.403452 0.300000 2400 1.428571
97.939712 0.400000 3200 1.666667
142.381740 0.500000 4000 2.000000
162.678710 0.550000 4400 2.222222
183.896175 0.600000 4800 2.500000
203.870917 0.650000 5200 2.857143
222.808221 0.700000 5600 3.333333
241.782645 0.750000 6000 4.000000
252.824780 0.775000 6200 4.444444
279.751398 0.800000 6400 5.000000
307.471717 0.825000 6600 5.714286
339.415889 0.850000 6800 6.666667
371.413354 0.875000 7000 8.000000
390.505284 0.887500 7100 8.888889
408.344121 0.900000 7200 10.000000
427.964702 0.912500 7300 11.428571
453.307363 0.925000 7400 13.333333
483.224073 0.937500 7500 16.000000
504.911659 0.943750 7550 17.777778
526.433221 0.950000 7600 20.000000
554.693406 0.956250 7650 22.857143
583.532213 0.962500 7700 26.666667
612.195055 0.968750 7750 32.000000
629.163420 0.971875 7775 35.555556
647.068860 0.975000 7800 40.000000
667.629935 0.978125 7825 45.714286
691.831905 0.981250 7850 53.333333
729.039830 0.984375 7875 64.000000
748.329730 0.985938 7888 71.113640
768.471540 0.987500 7900 80.000000
788.390297 0.989062 7912 91.424392
807.614078 0.990625 7925 106.666667
831.889128 0.992188 7938 128.008193
845.000015 0.992969 7944 142.227279
865.313345 0.993750 7950 160.000000
887.424404 0.994531 7956 182.848784
909.572865 0.995313 7963 213.356091
945.882794 0.996094 7969 256.016385
964.014513 0.996484 7972 284.414107
985.114464 0.996875 7975 320.000000
1021.571080 0.997266 7978 365.764448
1057.934456 0.997656 7981 426.621160
1093.910902 0.998047 7984 512.032770
1110.100395 0.998242 7986 568.828214
1126.289888 0.998437 7987 639.795266
1142.562404 0.998633 7989 731.528895
1158.751897 0.998828 7991 853.242321
1174.941389 0.999023 7992 1023.541453
1194.670357 0.999121 7993 1137.656428
1222.226880 0.999219 7994 1280.409731
1249.502214 0.999316 7995 1461.988304
1277.058738 0.999414 7995 1706.484642
1304.615261 0.999512 7996 2049.180328
1318.393523 0.999561 7996 2277.904328
1331.890595 0.999609 7997 2557.544757
1345.668857 0.999658 7997 2923.976608
1385.470751 0.999707 7998 3412.969283
1464.641730 0.999756 7998 4098.360656
1503.419352 0.999780 7998 4545.454545
1543.812709 0.999805 7998 5128.205128
1582.590332 0.999829 7999 5847.953216
1622.983688 0.999854 7999 6849.315068
1661.761311 0.999878 7999 8196.721311
1681.150122 0.999890 7999 9090.909091
1700.538933 0.999902 7999 10204.081633
1721.543478 0.999915 7999 11764.705882
1740.932290 0.999927 7999 13698.630137
1757.897500 0.999939 8000 16393.442623
1757.897500 0.999945 8000 18181.818182
1757.897500 0.999951 8000 20408.163265
1757.897500 0.999957 8000 23255.813953
1757.897500 0.999963 8000 27027.027027
1757.897500 0.999969 8000 32258.064516
1757.897500 0.999973 8000 37037.037037
1757.897500 0.999976 8000 41666.666667
1757.897500 0.999979 8000 47619.047619
1757.897500 0.999982 8000 55555.555556
1757.897500 0.999985 8000 66666.666667
1757.897500 0.999986 8000 71428.571429
1757.897500 0.999988 8000 83333.333333
1757.897500 0.999989 8000 90909.090909
1757.897500 0.999991 8000 111111.111111
1757.897500 0.999992 8000 125000.000000
1757.897500 0.999993 8000 142857.142858
1757.897500 0.999994 8000 166666.666668
1757.897500 0.999995 8000 199999.999999
1757.897500 0.999996 8000 250000.000000
1757.897500 0.999997 8000 333333.333336
1757.897500 0.999998 8000 500000.000013
1757.897500 0.999999 8000 999999.999971
1757.897500 1.000000 8000 10000000.000000新的demo
动态访问部分写的有点问题,新demo可以实现targeter的计数效果。
服务端代码与之前一致
id.txt
TRA_1_index
TRA_2_index
TRA_3_index
TRA_4_index
TRA_5_index压测端
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
vegeta "github.com/tsenart/vegeta/v12/lib"
)
func main() {
rate := vegeta.Rate{Freq: 100, Per: time.Second}
duration := 4 * time.Second
targeter := NewCustomTargeter(vegeta.Target{
Method: "GET",
URL: "http://localhost:8080/test",
})
//测试的实现需要基于Attacker
attacker := vegeta.NewAttacker()
var metrics vegeta.Metrics
for res := range attacker.Attack(targeter, rate, duration, "random") {
metrics.Add(res)
}
metrics.Close()
fmt.Printf("99th percentile: %s\n", metrics.Latencies.P99)
}
func NewCustomTargeter(target vegeta.Target) vegeta.Targeter {
//读取id文件
idData, err := readRealData()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//cachedArray := make([]bool, len(idData))
x := 0
return func(tgt *vegeta.Target) error {
//其中,tgt是作为指针传入的,是需要被修改的。后续HTTP请求的赋值都是来自tgt,所以看做是另外一个返回值会更好一些
*tgt = target
//tgt.URL += "/custom" + strconv.Itoa(rand.Intn(100))
tgt.URL += "/" + idData[x]
x++
if x >= len(idData) {
x = 0
}
//tgt.Header = http.Header{}
return nil
}
}
func readRealData() ([]string, error) {
//读取id.txt文件
filePath := "id.txt"
file, err := os.OpenFile(filePath, os.O_RDONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer file.Close()
//数据格式为音频id,字符串`TRA_{albumid}_index`,albumid为6-10位数字,index为5位数字以内
//将其作为字符串读取并写入到slices中
idData := make([]string, 0, 1400000)
buf := bufio.NewReader(file)
for {
line, err := buf.ReadString('\n')
line = strings.TrimSpace(line)
idData = append(idData, line)
if err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
} else {
return nil, err
}
}
}
return idData, nil
}服务端部分的结果是
2022-06-07 16:55:49|14.132µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_1_index|::1|name=TRA_1_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|20.895µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_2_index|::1|name=TRA_2_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|20.918µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_3_index|::1|name=TRA_3_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|21.048µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_4_index|::1|name=TRA_4_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|12.286µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_5_index|::1|name=TRA_5_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|28.04µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_1_index|::1|name=TRA_1_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|49.178µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_2_index|::1|name=TRA_2_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|29.287µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_3_index|::1|name=TRA_3_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|45.1µs|200|GET|/test/TRA_4_index|::1|name=TRA_4_index|0 B|0 B||
2022-06-07 16:55:49|17.428µs|200|GET具体的|/test/TRA_5_index|::1|name=TRA_5_index|0 B|0 B||这样就可以实现对id.txt中每一行数据的遍历,targeter范例在压测端的NewCustomTargeter,其中的x可以视为一个闭包实现的静态变量